MEDICAL TERMS
HOW DOES IMPOTENCE VACUUM PUMPS WORK?
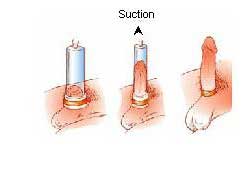
Impotence vacuum pumps create an erection by using a plastic cylinder which is placed around the penis. A manual or electronic pump gradually withdraws the air from the cylinder, creating a vacuum and drawing blood into the penis. Once the penis is rigid, the cylinder is removed and an elasticized band (often referred to as a "tension ring") is applied to the base of the penis to prevent blood from flowing back into the body and to maintain the erection during intercourse.
The diagram on the right clearly demonstrates how an impotence vacuum pump works.
NOTE: The tension ring should never be left on for more than 30 minutes
VARICOCELECTOMY
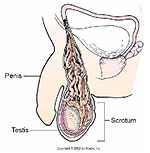
A varicocele is a mass of enlarged and dilated veins that develops within the scrotum. These veins are blood vessels that drain the testicles. If the valves that regulate bloodflow from these veins are defective, blood does not circulate from the testicles efficiently, causing swelling in the veins above and behind the testicles with resulting warming of the testes. This warming effect can affect testicular growth and sperm quality. Sometimes patients experience a vague heaviness or discomfort in the affected scrotum. Many varicoceles do not cause symptoms and are discovered only when the patient sees a doctor for fertility issues.
Varicoceles are classified according to how visible they are. The more visible, the higher the grade and the more likely to have symptoms:
Subclinical: Not felt or seen by the doctor. Detected only by Dopppler ultrasound examination.
Grade 1: Felt when the patient strains hard but not otherwise visible
Grade 2: Can be felt without the patient straining hard but still not visible
Grade 3: Easily seen and felt. Commonly described as a “bag of worms”.
Varicocelectomy is the most common surgical procedure for infertility in males. This operation improves semen quality in about two-thirds of men and basically doubles the chance of conception. The operation is usually performed through a small groin incision as a dayprocedure. Laparoscopic varicocelectomy is also performed but has no clear cut advantage over a small inguinal incision. Complications following varicocelectomy include hydrocele formation, epididymitis, injury to the internal spermatic artery and persistent or recurrent scrotal varicoceles. Fortunately, this occurs in less than 3-5% of patients.
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF EJACULATORY DUCT
Sometimes the exit site of the "sperm" transporting tube (vas deferens) is blocked. Under anesthesia they are inspected using a scope and then can be incised or unroofed. In select cases, this transurethral resection of the ejaculatory ducts has resulted in marked improvement in semen parameters, and pregnancies have been achieved.
SPERM RETRIEVAL
In cases where the blockage is not remediable and sperm can be retrieved for assisted reproduction.
Return