MEDICAL TERMS
BLADDER TRAINING
Perhaps the best first-line approach for any form of incontinence is a combination of Kegel exercises and bladder training. In one study, women who used this combination approach experienced an average 50% reduction in incontinence episodes, with nearly 40% of them achieving complete continence. It was equally effective for urge, stress, or mixed incontinence.
Patients start by planning short intervals between urinations and then gradually progressing with the ultimate goal of voiding every three to four hours. Bladder retraining gradually prolongs the time between visits to the toilet and is usually taught with urge suppression strategies. At Pearllyn Quek Urology, patients undergo a supervised 3 month program that has a proven success rate of 80%. Adjuncts like medications, electrical stimulation or biofeedback may be used. Patients record their progress on a voiding diary and goals are laid out and regularly reviewed. With or without medication, bladder training has helped many people overcome urinary urgency, frequency and incontinence and is thought to have a longer lasting impact than medications alone.
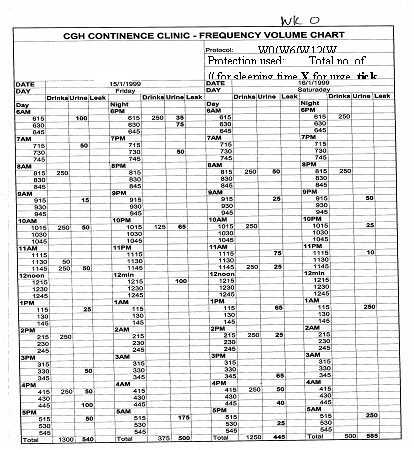
These bladder diaries show the improvement in urinary frequency and voided volumes before (left chart) and after(right chart) bladder retraining.
PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING
Perhaps the best first-line approach for any form of incontinence is a combination of Kegel exercises and bladder training. In one study, women who used this combination approach experienced an average 50% reduction in incontinence episodes, with nearly 40% of them achieving complete continence. It was equally effective for urge, stress, or mixed incontinence.
Studies also reported that between 50% and 75% of patients who perform only pelvic floor exercises experience a substantial improvement in their symptoms, including elderly people who have had the problem for years.
Kegel’s or Pelvic floor muscle exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor that support the bladder and close the sphincters. Dr. Kegel first developed these exercises to assist women before and after childbirth, but they are very useful in helping to improve continence for both men and women. Studies indicate that such exercises are very effective, even for men recovering from surgery for prostate cancer.
Kegel exercises are particularly useful for the following:
 Stress incontinence. Some experts believe that Kegel exercises should be the primary treatment for stress incontinence.
Stress incontinence. Some experts believe that Kegel exercises should be the primary treatment for stress incontinence.
 Urge incontinence. They can also be helpful for urge incontinence in cases that are not caused by nerve damage. In one study, 85% of women reported satisfaction with this program.
Urge incontinence. They can also be helpful for urge incontinence in cases that are not caused by nerve damage. In one study, 85% of women reported satisfaction with this program.
At Pearllyn Quek Urology, your pelvic floor contraction efforts will be assessed and graded before starting your PFMT program. This grading, along with your clinical progress will be reviewed over 3 months.
Rating
Contraction
Duration
2
Slight Squeeze
Not Sustained
3
Moderate Squeeze
2 to 3 Secs.
4
Good Squeeze
3 to 5 Secs.
5
Strong Squeeze
More than 5 Secs.
Grading of the pelvic floor muscle using the modified Oxford Scale(Laycock 1994)
It will usually take 3 months before a patient sees significant improvement.
Incontinence will return to its original severity if these exercises are discontinued, so commitment to the program must be high and possibly life-long.
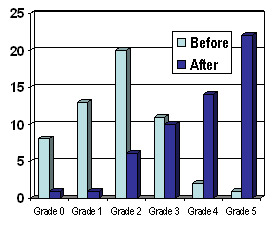
These bar charts show how the majority of our patients improve from Grades 0-3 (poor or unsustained contractions) to grades 3-5 (dark blue bars) at the end of our 3 months program.
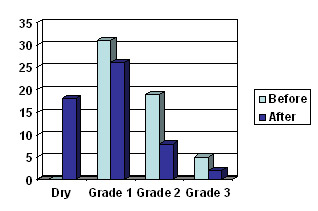
Dark blue bars – After PFMT
Light blue bars – Before PFMT
Grade 1 = Mild, occasional stress incontinence that does not require surgery
Grade 2 = Moderate stress incontinence often requiring surgery
Grade 3 = Severe daily stress incontinence definitely requiring surgery
This bar chart shows how the majority of patients undergoing our pelvic floor training are cured (dry) or improved (shifted to Gd 1) compared to before (light blue bars)
BIOFEEDBACK

Biofeedback involves using visual, sound or tactile feedback to re-inforce teaching of physiological functions. In patients unable to do proper Kegel’s exercise, biofeedback is utilized with a graphical analysis of pelvic muscle contractions conveyed via a small vaginal probe (above). The results can be analyzed graphically and compared over time to ensure that you are improving. At Pearllyn Quek Urology, we have a scheduled program for biofeedback that allows us to monitor our patients and ensure that pelvic floor strengthening and clinical improvement is achieved.
FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION
For patients with weak pelvic floor muscles, electrical stimulation is usually added to supplement other treatments. Electrical stimulation involves placing a small, transvaginal probe that provides a very low amplitude, painless electrical current to stimulate the muscles by creating a rhythmic contraction of the pelvic floor musculature. This technique helps with the training and response that patient get with pelvic floor exercises.
Small amplitude , painless electrical current is also utilized to treat urinary urgency, frequency and pelvic pain. At Pearllyn Quek Urology, we have a scheduled program for electrical stimulation that allows us to monitor our patients and ensure that pelvic floor strengthening and clinical improvement is achieved.
URODYNAMIC STUDY (UDS)
This is a test that measures the pressure in the bladder and the flow of urine through the urethra. It provides information about how much urine the bladder can hold and allows your doctor to assess the efficacy of your bladder in storing and voiding urine. Sometimes, urodynamics is done together with x-ray screening, where live images produced on a TV monitor show the doctor what is happening when your bladder is filling and emptying. The screening is known as video-urodynamics (VUDS). Both routine (without x-ray) and video-urodynamics involve the insertion of very fine tubes into the urethra and rectum. The study forms part of the total assessment of your bladder problems from which your doctor can plan appropriate therapy.
BOTOX
this is the most common commercial form of Botulinum A Toxin. Botulinum A Toxin is a toxin purefied from bacteria. It prevents the nerve endings in muscles from sending the signals to contract. As a result, muscles become paralysed, flaccid and may shrink in size from disuse.This fact is exploited by plastic surgeons to well known effect. It is also used by neurologists who treat patients with muscle spasticity. The amount of paralysis is dose related. It takes about 28,000 units of toxin to kill an adult. Doses used for medical purposes range from 20-300 units and are very safe. The use of Botulinum A Toxin for urological conditions is not FDA approved yet.
This is because trials with numbers large enough to provideproof of effect are yet to be concluded. However, it is used in Europe and Asia, usually in the context of clinical trials, to treat urge incontinence and voiding disorders with very positive results.
BIOFEEDBACK
Biofeedback involves using visual, sound or tactile feedback to re-inforce teaching of physiological functions. In patients unable to do proper Kegel’s exercise, biofeedback is utilized with a graphical analysis of pelvic muscle contractions conveyed via a small vaginal probe (above). The results can be analyzed graphically and compared over time to ensure that you are improving. At Pearllyn Quek Urology, we have a scheduled program for biofeedback that allows us to monitor our patients and ensure that pelvic floor strengthening and clinical improvement is achieved.
URODYNAMIC STUDY (UDS)
This is a test that measures the pressure in the bladder and the flow of urine through the urethra. It provides information about how much urine the bladder can hold and allows your doctor to assess the efficacy of your bladder in storing and voiding urine. Sometimes, urodynamics is done together with x-ray screening, where live images produced on a TV monitor show the doctor what is happening when your bladder is filling and emptying. The screening is known as video-urodynamics (VUDS). Both routine (without x-ray) and video-urodynamics involve the insertion of very fine tubes into the urethra and rectum. The study forms part of the total assessment of your bladder problems from which your doctor can plan appropriate therapy.
Return