MEDICAL TERMS
TRANSURETHAL RESECTION OF BLADDER TUMORS (TURBT)
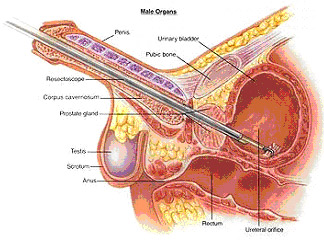
Transurethral resection of bladder: This picture shows a "resectoscope" being inserted into the bladder through the penis. The tumor is then removed using a loop with cutting current.
FUNCTIONAL ELECTRICAL STIMULATION
For patients with weak pelvic floor muscles, electrical stimulation is usually added to supplement other treatments. Electrical stimulation involves placing a small, transvaginal probe that provides a very low amplitude, painless electrical current to stimulate the muscles by creating a rhythmic contraction of the pelvic floor musculature. This technique helps with the training and response that patient get with pelvic floor exercises.
Small amplitude , painless electrical current is also utilized to treat urinary urgency, frequency and pelvic pain. At Pearllyn Quek Urology, we have a scheduled program for electrical stimulation that allows us to monitor our patients and ensure that pelvic floor strengthening and clinical improvement is achieved.
BOTOX
this is the most common commercial form of Botulinum A Toxin. Botulinum A Toxin is a toxin purefied from bacteria. It prevents the nerve endings in muscles from sending the signals to contract. As a result, muscles become paralysed, flaccid and may shrink in size from disuse.This fact is exploited by plastic surgeons to well known effect. It is also used by neurologists who treat patients with muscle spasticity. The amount of paralysis is dose related. It takes about 28,000 units of toxin to kill an adult. Doses used for medical purposes range from 20-300 units and are very safe. The use of Botulinum A Toxin for urological conditions is not FDA approved yet.
This is because trials with numbers large enough to provideproof of effect are yet to be concluded. However, it is used in Europe and Asia, usually in the context of clinical trials, to treat urge incontinence and voiding disorders with very positive results.
TRANSURETHRAL RESECTION OF PROSTATE (TURP)
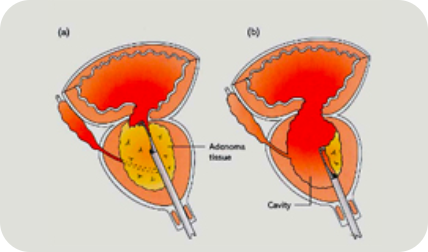
(TURP) remains the gold standard in treating BPE. In TURP, the surgeon inserts a telescopic tube up the urethra and cuts out pieces of the prostate with a wire loop till the urethra becomes widely patent. After a TURP, one may expect the urinary stream to become much more forceful and fast. However, the symptoms of urinary frequency or waking up to go too many times at night may remain in up to 30% of patients.
A TURP generally requires a 2 day stay. This procedure is painless under general or regional anesthesia. Upon discharge, patients should expect to pass out urine with blood for days to weeks after the procedure. Occassionally, patients also experience a temporary difficulty in controlling their bladder immediately after the TURP. This should resolve in weeks.
One of the bothersome side effects of a TURP is that there is a 70-90% chance of retrograde ejaculation. Ejaculated sperm will go "backwards" into the bladder instead of shooting forwards. This is because the bladder neck does not close during ejaculation as it normally should as it has been cut in a TURP. Because of this, and the perception that it is a major operation, several minimally invasive alternatives to TURP are available. While these may have fewer side effects they may not be as effective or durable.
MINIMALLY INVASIVE OPTIONS TO TURP
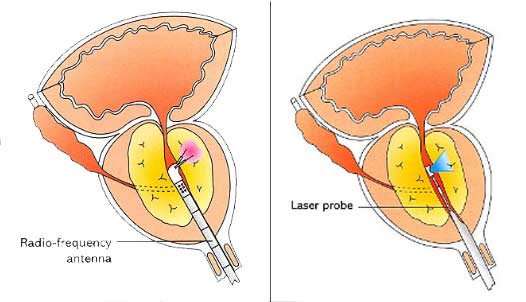
There are a few alternatives for patients who do not wish to undergo a TURP. These include radiofrequency ablation (TUNA) or laser vaporization of the prostate. These are less invasive in terms of the amount of tissue removed and the creation of raw exposed areas that are prone to bleeding. This translates to less bleeding and shorter healing times. The results are usually not as dramatic or durable as a TURP but may be satisfactory for some patients.
Transurethral Needle Ablation (TUNA) of Prostate destroys a small volume of prostate at area of application and also destroys some nerves so that the prostate becomes more "relaxed". The "opening up" effect is not as complete as a TURP and recurrence is common.
Greenlight Laser ablation of Prostate which vaporizes the prostatic tissue in a controlled manner to remove the obstructing prostatic lobe.
RADICAL PROSTATECTOMY
Radical prostatectomy involves surgically removing the prostate gland and the seminal vesicles. It is the most common treatment for localized cancer of the prostate in men under 70 who do not have other health complications.
It is performed through a lower abdominal incision (Open) or laparoscopically. During a laparoscopic prostatectomy, a telescopic instrument called a laparoscope is inserted into the abdomen through a small incision at the belly button. The laparoscope allows surgeons to view inside the abdomen and perform the surgery without having to make a large incision. Usually, four more small incisions are made in the abdomen to accommodate surgical instruments during surgery. This eliminates the need for a large surgical incision to remove the prostate. As a result, the patient may experience less pain and scarring, faster recovery and less risk of infection. In some cases, the surgical procedure may require conversion to the standard open operation if extreme difficulty is encountered during the laparoscopic procedure. Side effects of radical prostatectomy include:
 Risk of blood clots
Risk of blood clots
 Urinary leakage (incontinence)
Urinary leakage (incontinence)
 dysfunction (impotence)
dysfunction (impotence)
If the cancer is small, surgeons try to avoid removing or cutting the nerves that control a man's ability to achieve an erection (nerve sparing). Depending on the patient's age and the stage of tumor advancement, nerve-sparing techniques allow about 40 percent to 65 percent of men who were sexually potent before surgery to remain potent after surgery
TRUS (TRANSRECTAL ULTRASOUND ) BIOPSY
A Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) of the prostate gland is performed when
 a nodule is felt by a physician during a routine physical or prostate cancer screening exam
a nodule is felt by a physician during a routine physical or prostate cancer screening exam
 an elevated blood PSA test result is noted
an elevated blood PSA test result is noted
 evaluating a patient with male infertility
evaluating a patient with male infertility
In men, the prostate gland is located directly in front of the rectum, so the ultrasound exam is performed transrectally. The cylinder-shaped ultrasound probe is gently placed in the rectum as the patient lies on his left side with the knees bent
The ultrasound probe allows a needle to be advanced into the prostate gland while the urologist watches the ultrasound images. Your doctor will usually follow a set protocol on the site and number of biopsies to take as the prostate ultrasound image can look perfectly normal in early stage cancer. This ultrasound examination is usually completed within 20 minutes and is performed in the clinic or day suite. Preparation includes having an enema and taking some prescribed antibiotics the day before.
PELVIC FLOOR MUSCLE TRAINING
Perhaps the best first-line approach for any form of incontinence is a combination of Kegel exercises and bladder training. In one study, women who used this combination approach experienced an average 50% reduction in incontinence episodes, with nearly 40% of them achieving complete continence. It was equally effective for urge, stress, or mixed incontinence.
Studies also reported that between 50% and 75% of patients who perform only pelvic floor exercises experience a substantial improvement in their symptoms, including elderly people who have had the problem for years.
Kegel’s or Pelvic floor muscle exercises are designed to strengthen the muscles of the pelvic floor that support the bladder and close the sphincters. Dr. Kegel first developed these exercises to assist women before and after childbirth, but they are very useful in helping to improve continence for both men and women. Studies indicate that such exercises are very effective, even for men recovering from surgery for prostate cancer.
Kegel exercises are particularly useful for the following:
 Stress incontinence. Some experts believe that Kegel exercises should be the primary treatment for stress incontinence.
Stress incontinence. Some experts believe that Kegel exercises should be the primary treatment for stress incontinence.
 Urge incontinence. They can also be helpful for urge incontinence in cases that are not caused by nerve damage. In one study, 85% of women reported satisfaction with this program.
Urge incontinence. They can also be helpful for urge incontinence in cases that are not caused by nerve damage. In one study, 85% of women reported satisfaction with this program.
At Pearllyn Quek Urology, your pelvic floor contraction efforts will be assessed and graded before starting your PFMT program. This grading, along with your clinical progress will be reviewed over 3 months.
Rating
Contraction
Duration
2
Slight Squeeze
Not Sustained
3
Moderate Squeeze
2 to 3 Secs.
4
Good Squeeze
3 to 5 Secs.
5
Strong Squeeze
More than 5 Secs.
Grading of the pelvic floor muscle using the modified Oxford Scale(Laycock 1994)
It will usually take 3 months before a patient sees significant improvement.
Incontinence will return to its original severity if these exercises are discontinued, so commitment to the program must be high and possibly life-long.
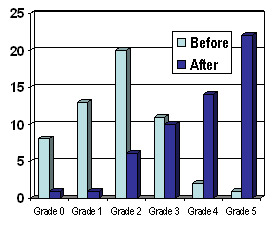
These bar charts show how the majority of our patients improve from Grades 0-3 (poor or unsustained contractions) to grades 3-5 (dark blue bars) at the end of our 3 months program.
Dark blue bars – After PFMT
Light blue bars – Before PFMT
Grade 1 = Mild, occasional stress incontinence that does not require surgery
Grade 2 = Moderate stress incontinence often requiring surgery
Grade 3 = Severe daily stress incontinence definitely requiring surgery
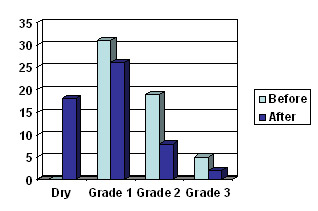
This bar chart shows how the majority of patients undergoing our pelvic floor training are cured (dry) or improved (shifted to Gd 1) compared to before (light blue bars)
Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy(ESWL)
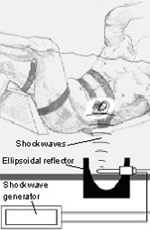
Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy is a technique for treating stones in the kidney and ureter that does not require surgery. Instead, high energy shock waves are aimed at the stone from outside the body and used to break stones into tiny fragments. These then pass from the body along with the urine.
Using x-rays or ultrasound to pinpoint the location of the stones, the body is positioned so that the stones are targeted precisely. About 2-4 thousand shock waves are needed to crush the stones. The complete treatment takes about 45 to 60 minutes.
The main advantage of this treatment is that many patients may be treated for kidney stones without surgery. However, not all types of kidney stones can be treated this way. In addition, sometimes the stone is not completely shattered and additional treatments are needed.
In patients thought to be good candidates for this treatment, about 70 to 90 percent are found to be free of stones within three months of treatment. The highest success rates occur in those patients with mobile stones that are located in the upper portions of the urinary tract (kidney and upper ureter). Your doctor will determine if your stone is suitable for shock wave therapy.
This is an outpatient day procedure. Most people can fully resume daily activities within one to two days. Drinking plenty of water helps the stone fragments pass. Most patients have some blood in the urine for a few days. Some abdominal pain may occur when the fragments pass down the urinary tract. This begins soon after treatment and may last for up to four to eight weeks. Oral pain medication and drinking lots of water will help relieve symptoms.
Ureteroscopy with stone fragmentation
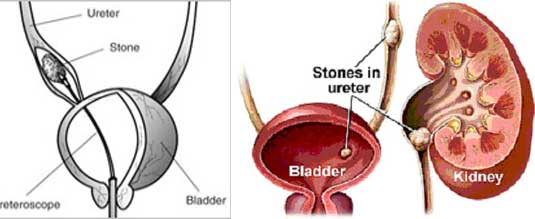
For stones found in the ureter,the doctor may pass a ureteroscope (a long thin tube-like device) up into the bladder and ureter. The stone is directly visualised and broken up using a laser or similar tool. The stone fragments are usually left to be passed out spontaneously.
PERCUTANEOUS NEPHROLITHOTRIPSY (PCNL)
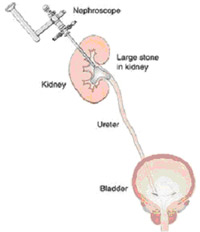
When kidney stones are more than 2 cm in diameter, a technique called percutaneous stone removal may be used. In this method, the surgeon makes a small incision in the back and a direct tract to the kidney is created under xray visualisation. The stone is then broken up and removed through this tract. This is performed under general anesthesia and requires a few days in the hospital.
OPEN PYELOLITHOTOMY
This is the traditional way in which kidney stones were removed. It entails having a large surgical wound through which the stone bearing portion of the kidney is opened up and the stone removed. While fairly quick and effective, the patient is left with a large wound and will need 6-8 weeks to resume normal activities. As there are usually more minimally invasive ways to break or remove a stone, this operation is seldom performed.
Return